

Hotline:0755-22277778
Tel:0755-22277778
Mobile:13826586185(Mr.Duan)
Fax:0755-22277776
E-mail:duanlian@xianjinyuan.cn
Advanced Institute of TechnologyShielding absorbing and thermally conductive materialsIntroduction: 6G, also known as the sixth generation mobile communication standard, is a conceptual wireless network mobile communication technology, also known as the sixth generation mobile communication technology. It mainly promotes the development of the Internet.
The 6G network will be a fully connected world that integrates ground wireless and satellite communication. By integrating satellite communication into 6G mobile communication, seamless global coverage can be achieved, and network signals can reach any remote village, allowing patients in deep mountainous areas to receive remote medical care and children to receive remote education. In addition, with the joint support of global satellite positioning systems, telecommunications satellite systems, Earth image satellite systems, and 6G ground networks, the ground to air full coverage network can also help humans predict weather and respond quickly to natural disasters. This is the future of 6G. 6G communication technology is no longer simply a breakthrough in network capacity and transmission speed. It is aimed at narrowing the digital divide and achieving the ultimate goal of the Internet of Things, which is the significance of 6G.
The data transmission rate of 6G may reach 50 times that of 5G, with latency reduced to one tenth of 5G. It is far superior to 5G in terms of peak speed, latency, traffic density, connection density, mobility, spectrum efficiency, positioning capability, and other aspects.
6G will use the terahertz (THz) frequency band, and the "densification" of 6G networks will reach an unprecedented level. At that time, our surroundings will be filled with small base stations. The terahertz frequency range refers to 100GHz-10THz, which is a frequency band much higher than 5G. The frequency of the wireless electromagnetic waves we use is constantly increasing from 1G (0.9GHz) to 4G (above 1.8GHz) in communication. Because the higher the frequency, the larger the bandwidth range allowed for allocation, and the larger the amount of data that can be transmitted per unit time, which is commonly referred to as "faster internet speed". However, another main reason for the upward development of frequency bands is the limited resources in the low-frequency range. Like a highway, even if it is wide, its capacity for vehicles is limited. When the road is not enough, vehicles will be blocked and unable to travel smoothly. At this time, it is necessary to consider developing another road. The same goes for spectrum resources. As the number of users and smart devices increases, limited spectrum bandwidth needs to serve more terminals, which can lead to a serious decline in service quality for each terminal. The feasible solution to this problem is to develop new communication frequency bands and expand communication bandwidth. The main 4G frequency bands of China's three major telecom operators are located in a portion of the frequency range between 1.8GHz and 2.7GHz, while the mainstream frequency band for 5G defined by the International Telecommunication Standards Organization is 3GHz-6GHz, which belongs to the millimeter wave frequency band. At 6G, we will enter the higher frequency terahertz band, and at this time, we will also enter the sub millimeter wave band. Gou Lijun, a researcher at the National Astronomical Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, told Internet Weekly: "Terahertz is called submillimeter in astronomy, and the stations of such observatories are generally high and dry, such as the Antarctic and the acatama desert in Chile? This involves the issue of the coverage range of the base station, that is, the transmission distance of the base station signal. Generally speaking, there are many factors that affect the coverage area of a base station, such as the frequency of the signal, the transmission power of the base station, the height of the base station, and the height of the mobile end. In terms of signal frequency, the higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength. Therefore, the diffraction ability of the signal (also known as diffraction, when encountering obstacles in the propagation of electromagnetic waves with a size close to the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave, the electromagnetic wave can be diffracted from the edge of the object. Diffraction can help with shadow diffraction and coverage of shaded areas) is poorer, and the loss is greater. And this loss will increase with the increase of transmission distance, and the coverage range of the base station will decrease accordingly. The frequency of 6G signals is already in the terahertz range, and this frequency is close to the spectrum of molecular rotational energy levels. It is easily absorbed by water molecules in the air, so the propagation distance in space is not as far as that of 5G signals. Therefore, 6G requires more base stations to "relay". The frequency band used by 5G is higher than that of 4G, and without considering other factors, the coverage area of 5G base stations is naturally smaller than that of 4G. In the higher frequency range of 6G, the coverage area of base stations will be smaller. Therefore, the base station density of 5G is much higher than that of 4G, and in the 6G era, the base station density will be unparalleled.

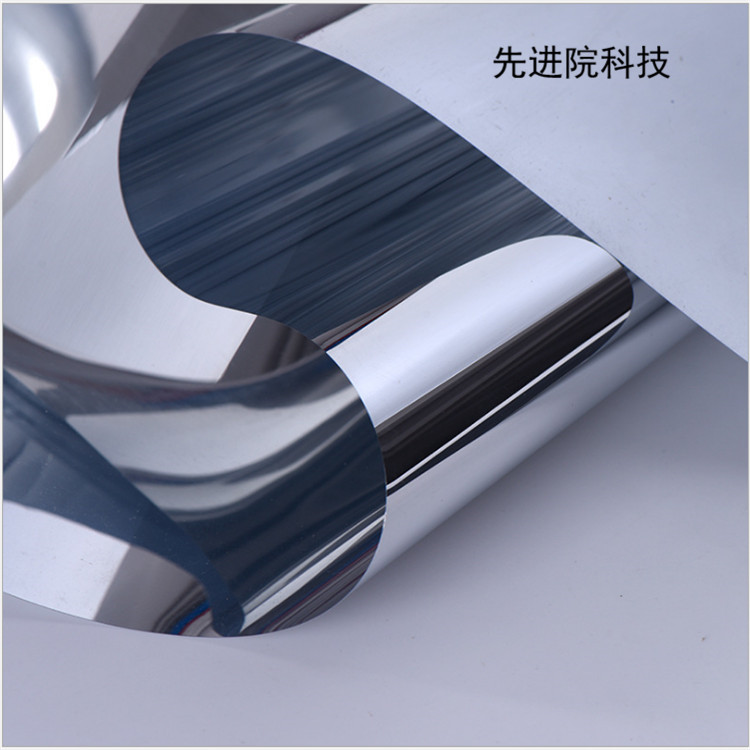
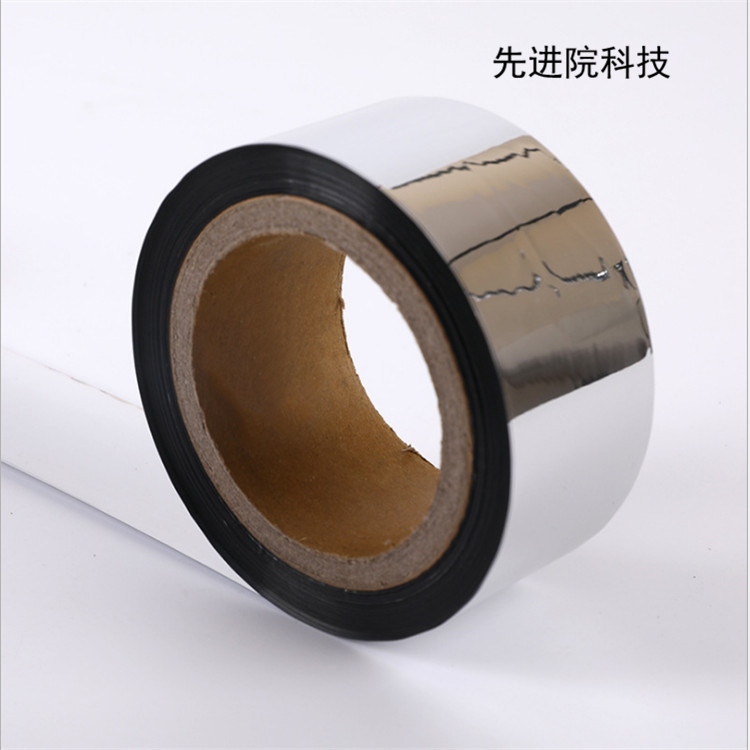

Advanced Institute (Shenzhen) Technology Co., Ltd, © two thousand and twenty-onewww.leird.cn. All rights reservedGuangdong ICP No. 2021051947-1 © two thousand and twenty-onewww.xianjinyuan.cn. All rights reservedGuangdong ICP No. 2021051947-2